Earthquakes are natural phenomena that occur when the Earth’s crust shifts or moves suddenly, resulting in shaking or vibration of the ground. They are caused by the release of energy that has built up over time due to tectonic forces or volcanic activity.
The point within the Earth’s crust where the energy is released is called the earthquake’s hypocentre or focus, and the point on the Earth’s surface directly above it is called the epicentre. Earthquakes also vary in size and intensity, with smaller earthquakes typically causing little damage and larger ones capable of causing widespread destruction.
Earthquakes trigger tsunamis, landslides, and volcanic eruptions. These compound effects on the environment and humans
THE SCIENCE BEHIND EARTHQUAKES- UNDERSTANDING THE EARTH’S TREMORS
An earthquake is a geological event that happens when there is a sudden release of energy in the Earth’s crust, causing the ground to shake or vibrate. They can happen anywhere in the world, but they are most common along the edges of the Earth’s tectonic plates, which are large pieces of the Earth’s crust that move and interact with each other.
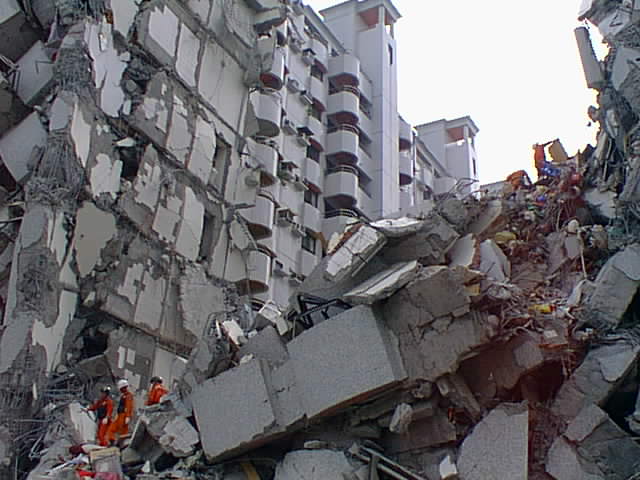

The science behind earthquakes involves understanding the concept of plate tectonics. The Earth’s crust is made up of several large plates that move relative to each other at a rate of a few centimetres per year. When two plates collide, one can be forced beneath the other in a process called subduction. The pressure and friction between the plates can cause them to become locked together, storing energy that is released suddenly in an earthquake when they finally slip past each other.
Earthquakes can also be caused by the movement of magma beneath the Earth’s surface, which can put pressure on the crust and cause it to move. Additionally, man-made activities like mining, drilling, and dam building can also trigger earthquakes.
Scientists use a variety of instruments to study earthquakes and their effects. Seismometers are instruments that measure the vibrations of the ground caused by earthquakes, and they can be used to determine the earthquake’s location, depth, and magnitude. Computer models are also used to simulate and predict the behaviour of earthquakes.
Understanding the science behind earthquakes is important for predicting and mitigating their effects. Building codes and infrastructure designs can be adapted to better withstand earthquakes, and early warning systems can give people time to take cover or evacuate in the event of an earthquake. Overall, knowledge about earthquakes can help us better prepare for and respond to these natural phenomena.
The Top 10 Most Seismically Active Countries in the World
Japan
Japan is situated on the Pacific Ring of Fire, a region that experiences a lot of seismic activity due to the collision of tectonic plates. It experiences thousands of earthquakes each year, with many of them being quite strong.
Indonesia
Indonesia is also located on the Pacific Ring of Fire and experiences frequent earthquakes due to the subduction of the Australian Plate beneath the Eurasian Plate.
Iran
Iran is located on the boundary of the Arabian Plate and the Eurasian Plate, making it a region of high seismic activity. In particular, Iran sits on a tectonic boundary, which makes it prone to seismic activity. As a result, it experiences frequent earthquakes, some of which have been quite devastating in the past.
Turkey
Turkey is located on the North Anatolian Fault, which is one of the world’s most active earthquake zones. Due to its location on the boundary of two tectonic plates, Iran is a region of high seismic activity. Consequently, it has experienced some of the deadliest earthquakes in history, including the devastating 1999 Izmit earthquake.
China
China is a large country with a varied topography that includes several active fault zones. Its southwestern region is particularly prone to earthquakes due to the collision of the Indian Plate with the Eurasian Plate.
Peru
Peru is located on the boundary of the Nazca Plate and the South American Plate, making it a region of high seismic activity. It experiences several earthquakes each year, many of which are strong.
Philippines
The Philippines is located on the Pacific Ring of Fire and experiences frequent earthquakes due to the collision of tectonic plates. It has experienced several deadly earthquakes in the past, including the 2013 Bohol earthquake.
Mexico
Mexico is located on the boundary of the North American Plate and the Pacific Plate, making it a region of high seismic activity. Several earthquakes occur each year, and the population strongly feels many of them.
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea is also located on the Pacific Ring of Fire and experiences frequent earthquakes due to the subduction of the Australian Plate beneath the Pacific Plate.
Italy
Italy is located on the boundary of the African Plate and the Eurasian Plate, making it a region of high seismic activity. It has experienced several deadly earthquakes in the past, including the 2016 Central Italy earthquake.
It’s important to note that while the above list includes some of the most notable earthquakes of the past five years, many other countries around the world also experience seismic activity, and there have likely been numerous other earthquakes that have occurred during this time period.
The Deadliest Earthquakes in History
Earthquakes have been a part of the Earth’s natural history for billions of years. Over time, many powerful and damaging earthquakes have occurred around the world. Earthquakes can be incredibly destructive, causing massive loss of life and property damage. Here are some of the deadliest earthquakes in recorded history
Tangshan Earthquake, China (1976)
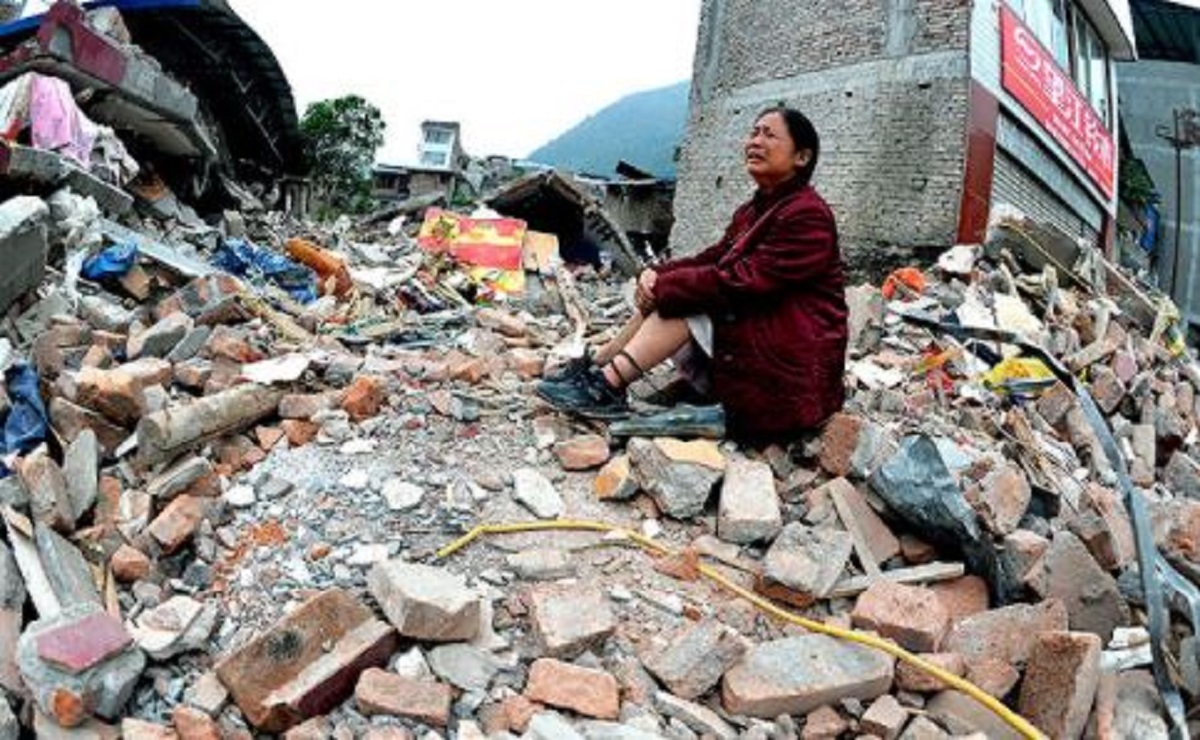

The Tangshan earthquake struck the city of Tangshan in north-eastern China and had a magnitude of 7.6. The earthquake and subsequent aftershocks killed an estimated 240,000 people.
Lisbon Earthquake, Portugal (1755)
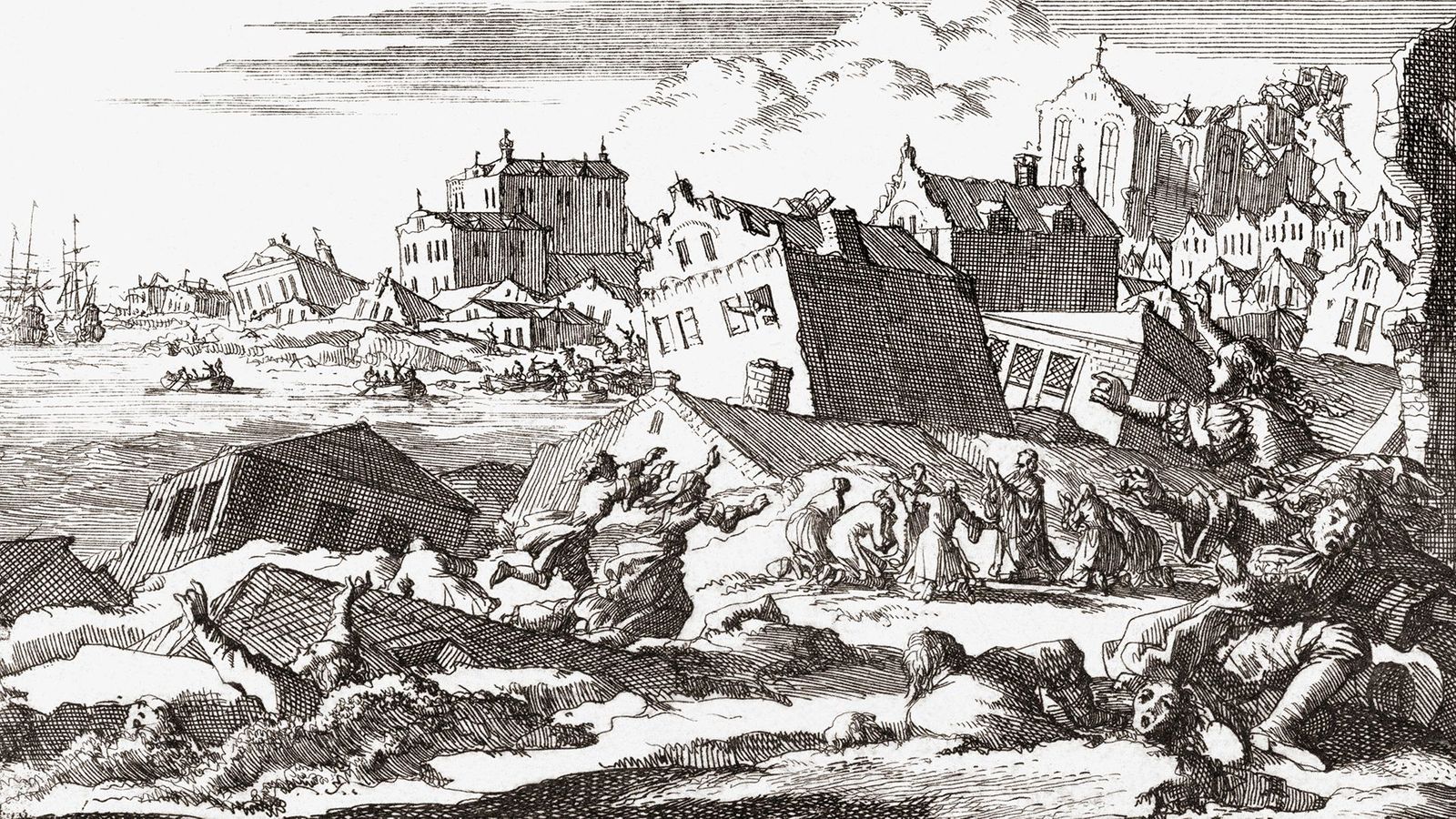

This earthquake had a magnitude of around 8.5 and caused widespread damage in Lisbon and other cities. The earthquake and subsequent tsunami killed an estimated 60,000 people.
Shaanxi Earthquake, China (1556)

This earthquake is believed to be the deadliest in history, with an estimated death toll of 830,000. The earthquake occurred in the Shaanxi province in central China and had a magnitude of around 8.0.
Aleppo Earthquake, Syria (1138)
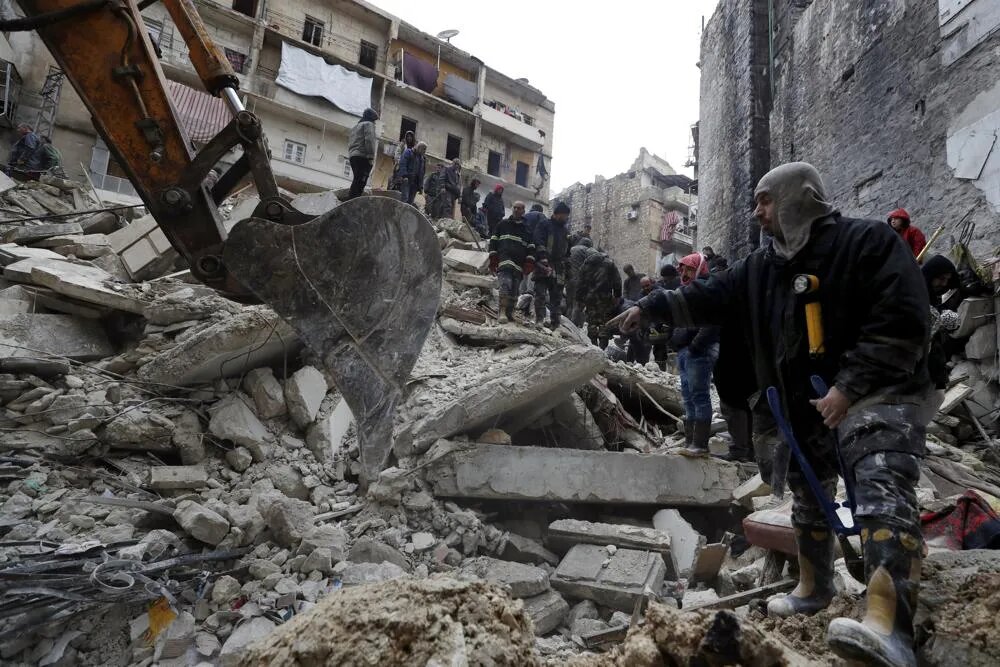

This earthquake had a magnitude of around 8.5 and struck the city of Aleppo in Syria, killing an estimated 230,000 people.
Sumatra Earthquake, Indonesia (2004)
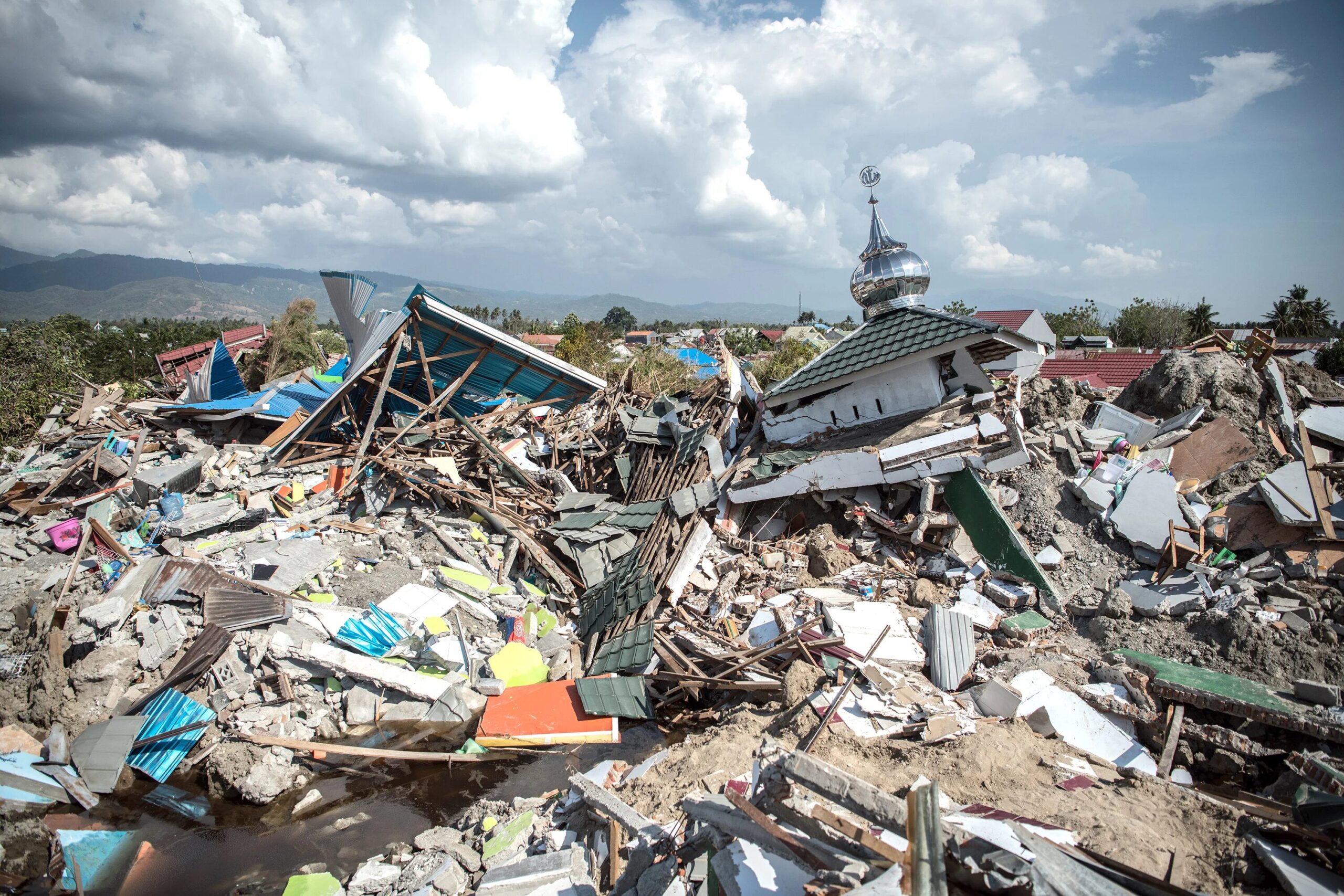

The Sumatra earthquake had a magnitude of 9.1 and triggered a massive tsunami that caused widespread devastation across the region. It is estimated to have killed around 230,000 people.
Haiyuan Earthquake, China (1920)
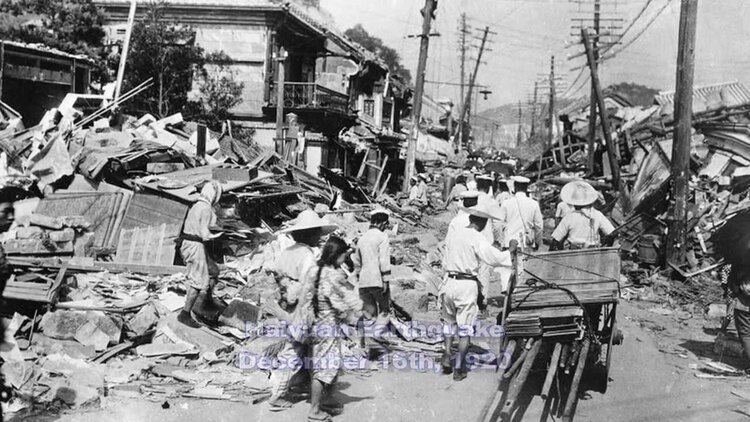

This earthquake had a magnitude of 8.5 and struck the Haiyuan County in China, killing an estimated 200,000 people.
Great Kanto Earthquake, Japan (1923)
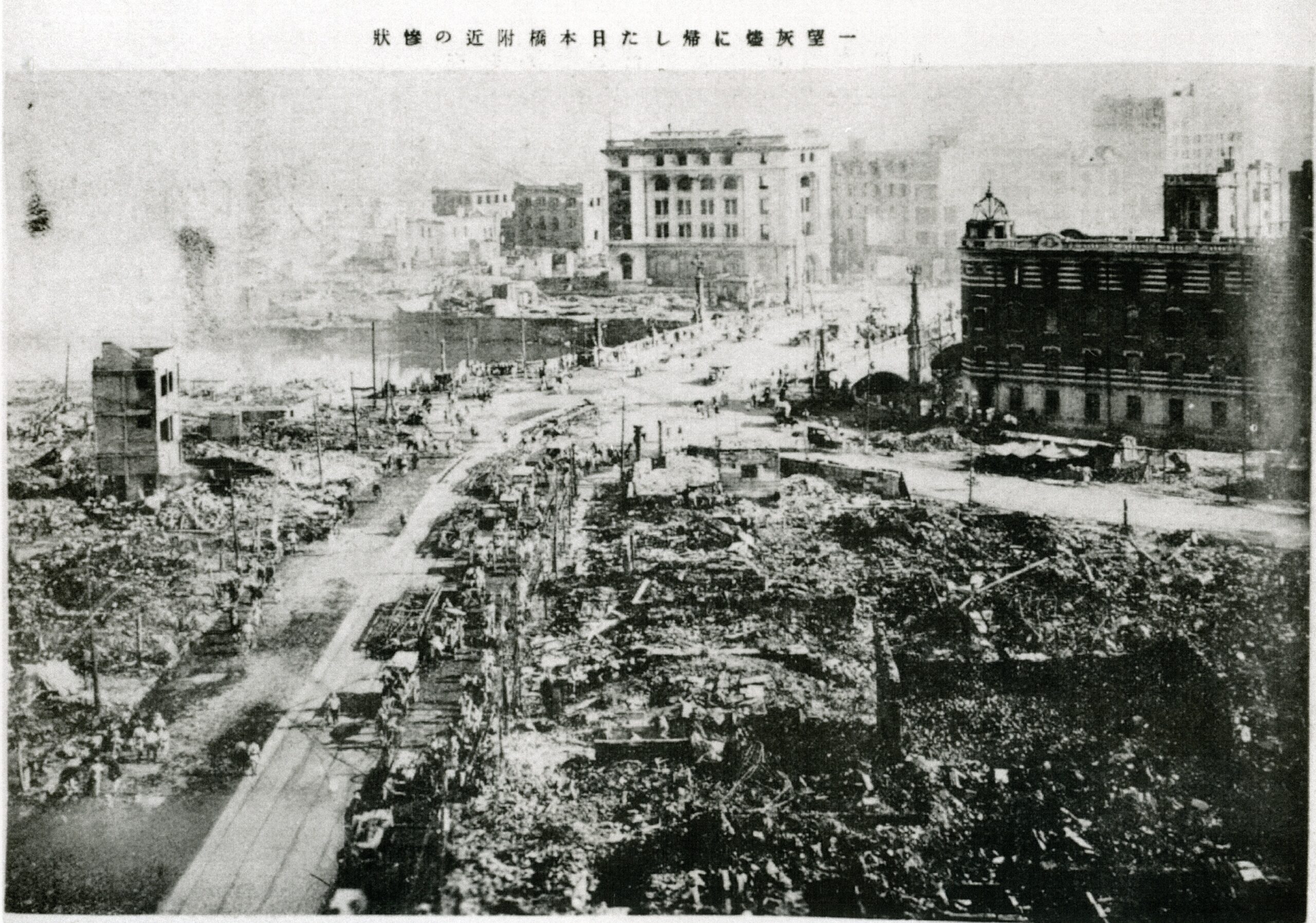

The Great Kanto earthquake, which had a magnitude of 7.9, struck the Kanto region of Japan, including the city of Tokyo. As a result of the earthquake and resulting fires, an estimated 142,800 people were killed.
Sichuan Earthquake, China (2008)

The Sichuan earthquake had a magnitude of 7.9 and struck the Sichuan province of China, killing an estimated 87,587 people.
Messina Earthquake, Italy (1908)
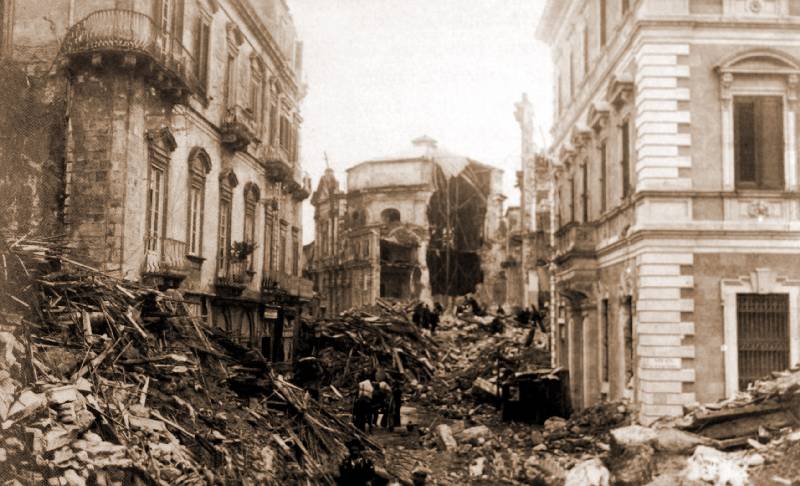

This earthquake had a magnitude of 7.1 and struck the city of Messina in Italy, killing an estimated 72,000 people.
Guatemala Earthquake (1976)
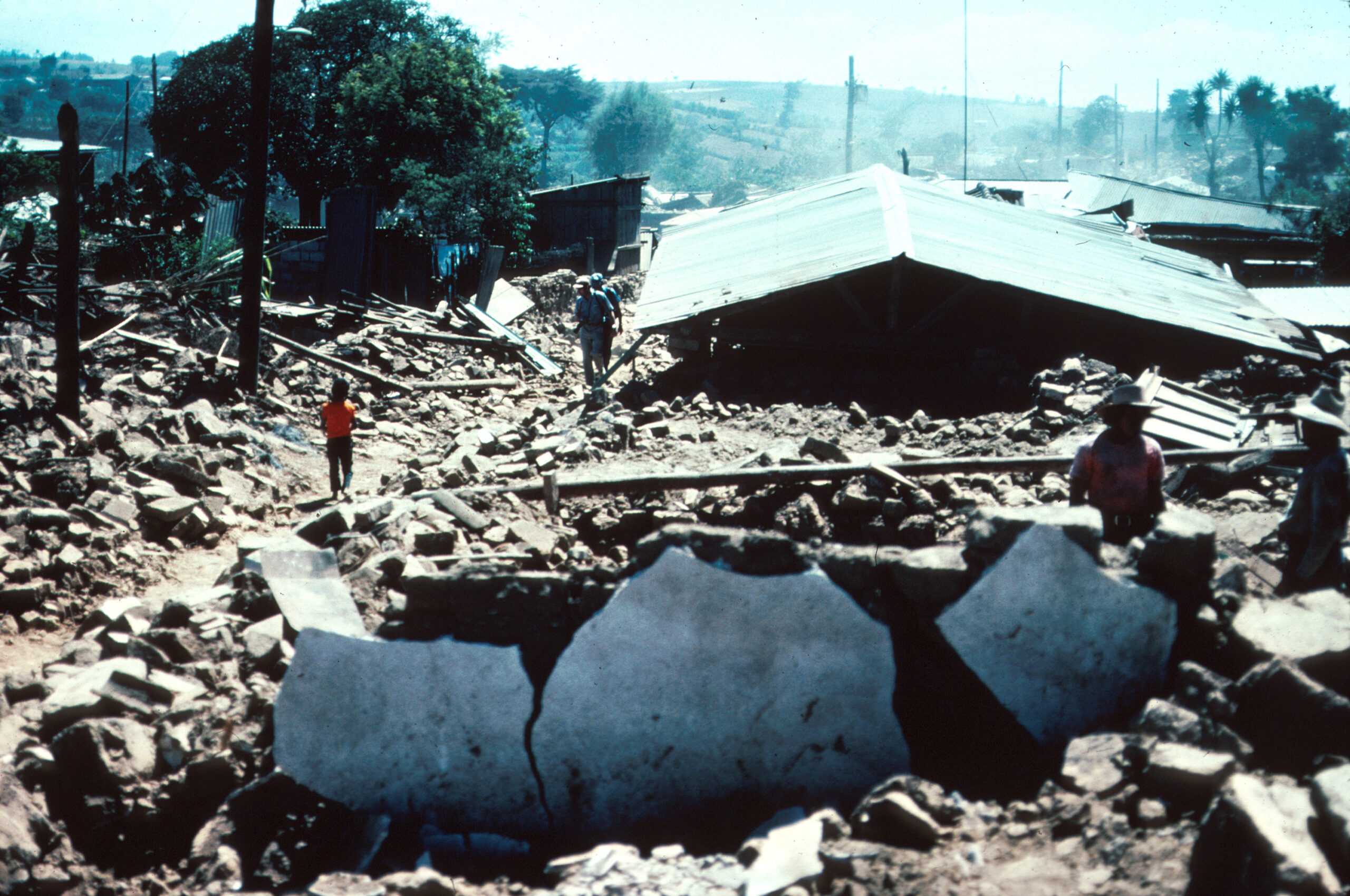

This earthquake had a magnitude of 7.5 and struck Guatemala, killing an estimated 23,000 people.
Haiti Earthquake (2010)
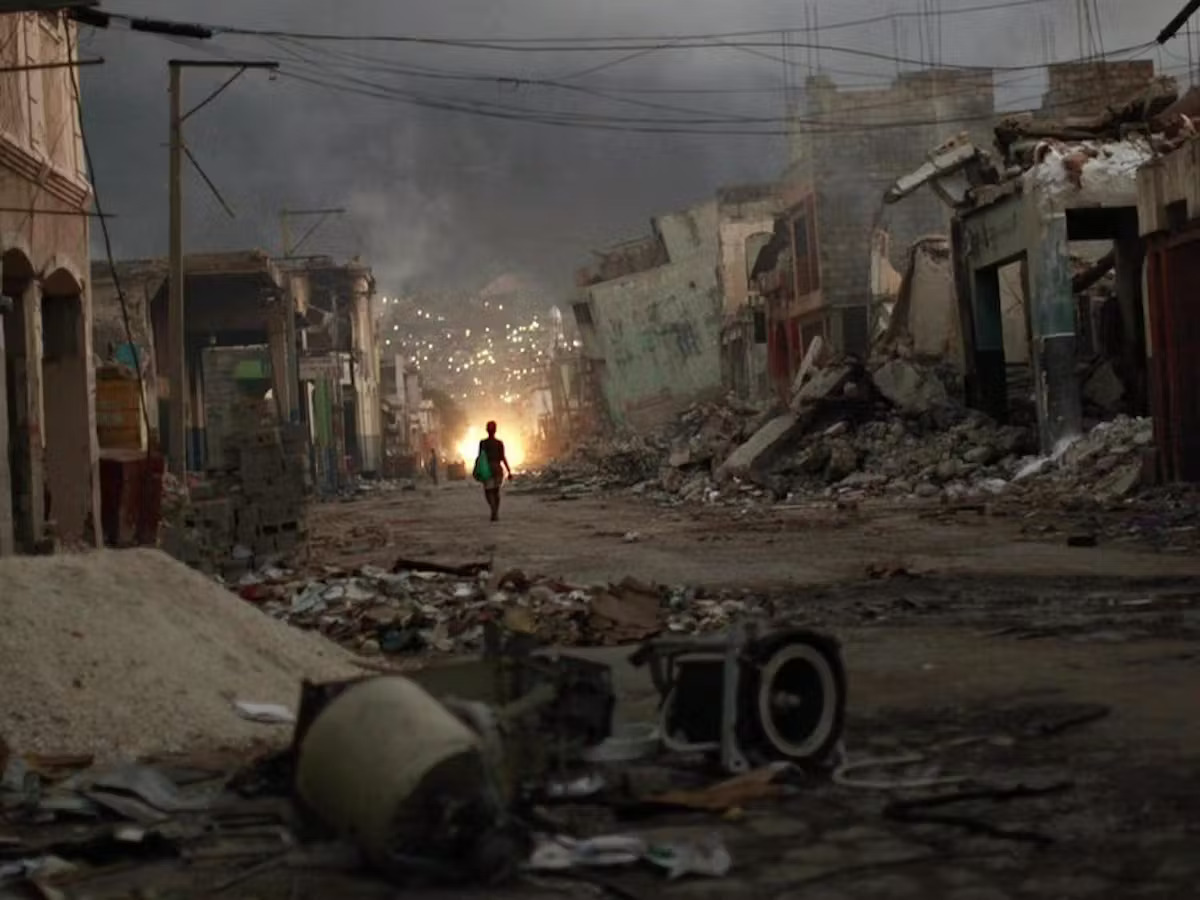

This earthquake had a magnitude of 7.0 and struck the island nation of Haiti, killing over 220,000 people and causing widespread damage to buildings and infrastructure.
Tohoku Earthquake and Tsunami, Japan (2011)

This earthquake had a magnitude of 9.0 and triggered a massive tsunami that devastated the north-eastern coast of Japan. The disaster killed over 15,000 people and caused extensive damage to buildings and infrastructure.
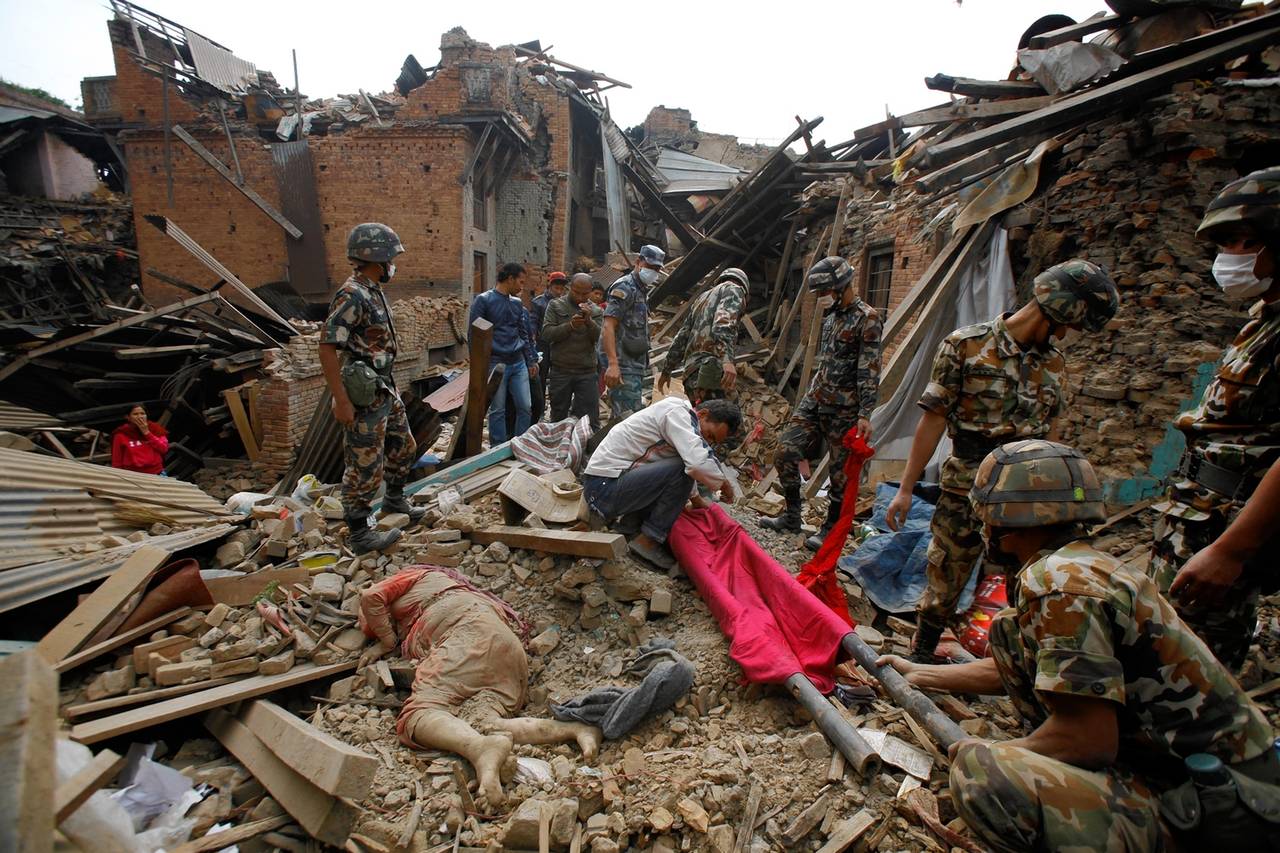
Nepal Earthquake (2015)

The Nepal earthquake had a magnitude of 7.8 and caused widespread destruction across the country, killing an estimated 8,000 people.
These earthquakes serve as reminder of the devastating power of nature and the importance of earthquake preparedness and response measures.
EARTHQUAKE HAPPENED IN LAST FIVE YEARS
2021 Sulawesi Earthquake, Indonesia
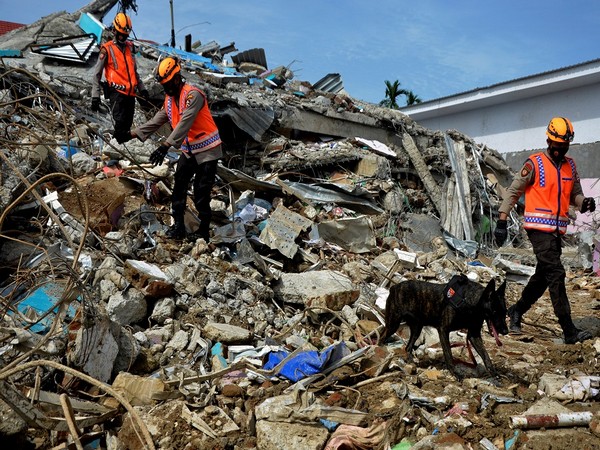

On January 15, 2021, a magnitude 6.2 earthquake struck the island of Sulawesi in Indonesia, killing at least 105 people and also injuring hundreds more. The earthquake also caused significant damage to buildings and infrastructure in the region.
2021 Assam Earthquake, India

On April 28, 2021, a magnitude 6.4 earthquake struck the state of Assam in northeast India, causing significant damage to buildings and infrastructure in the region. Therefore, the earthquake resulted in disruptions to the daily lives of many residents and a need for emergency response efforts.
2019 Ridgecrest Earthquakes, California, USA
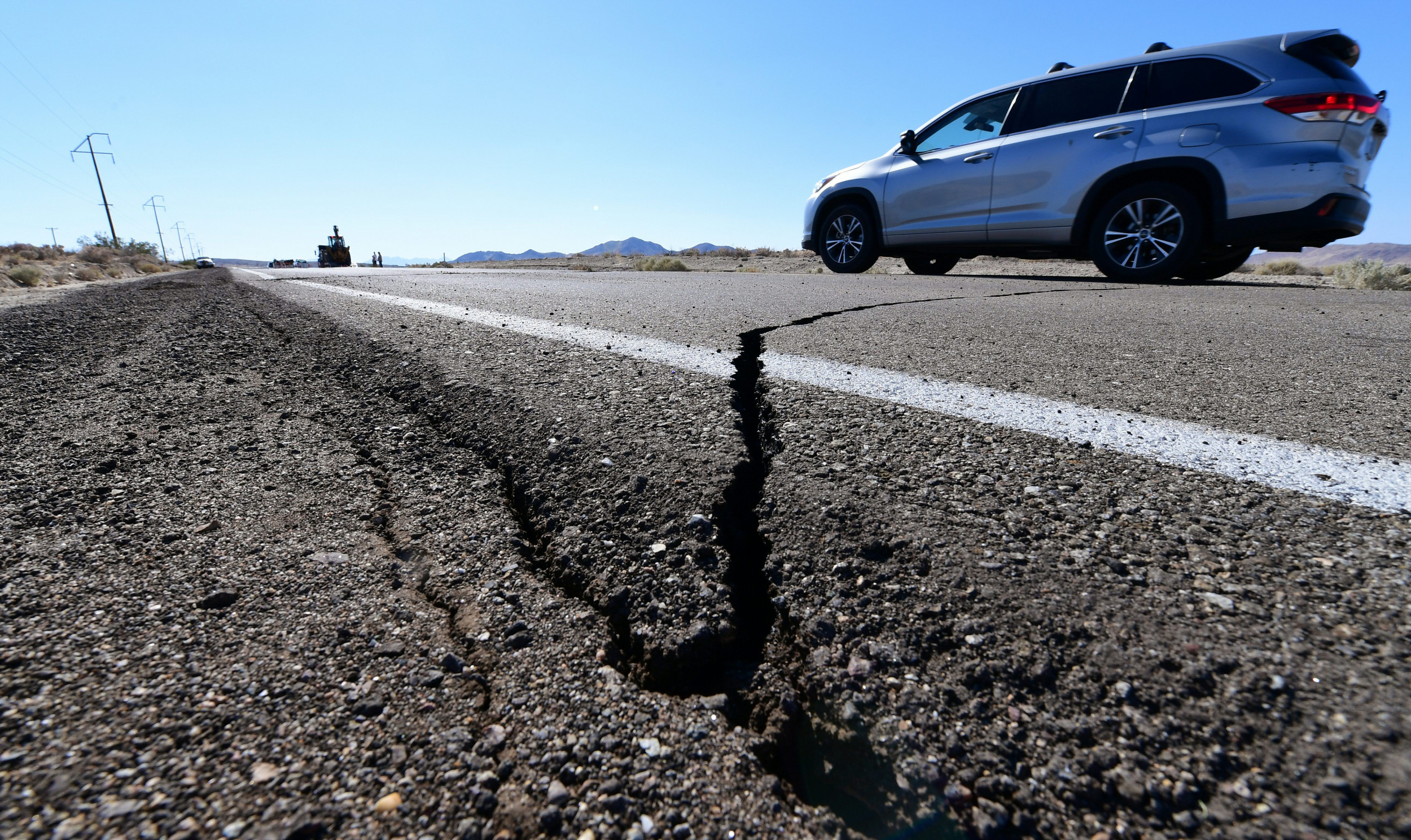

On July 4 and 5, 2019, a series of earthquakes struck the Ridgecrest area in Southern California, with the largest earthquake having a magnitude of 7.1. The earthquakes caused significant damage to buildings and infrastructure in the area but fortunately did not result in any fatalities.
2018 Sulawesi Earthquake and Tsunami, Indonesia
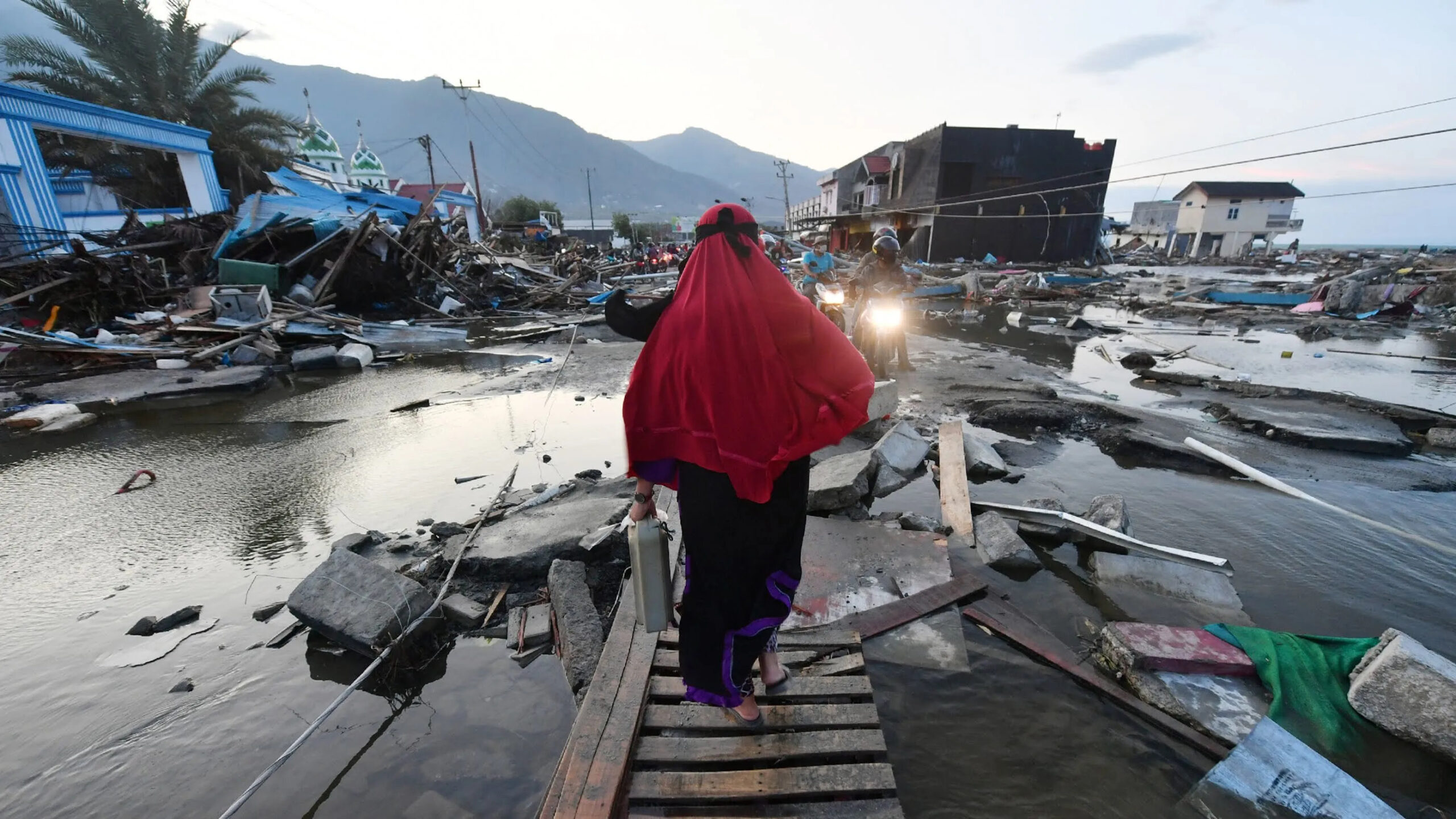

The earthquake struck the Indonesian island of Sulawesi on September 28, 2018, with a magnitude of 7.5, triggering a massive tsunami that devastated the region. The disaster claimed over 4,300 lives and caused extensive damage to buildings and infrastructure.
2017 Puebla Earthquake, Mexico

On September 19, 2017, a magnitude 7.1 earthquake struck the state of Puebla in central Mexico, killing over 300 people and also injuring thousands more. The earthquake caused extensive damage to buildings and infrastructure in the region.
2016 Manipur Earthquake, India
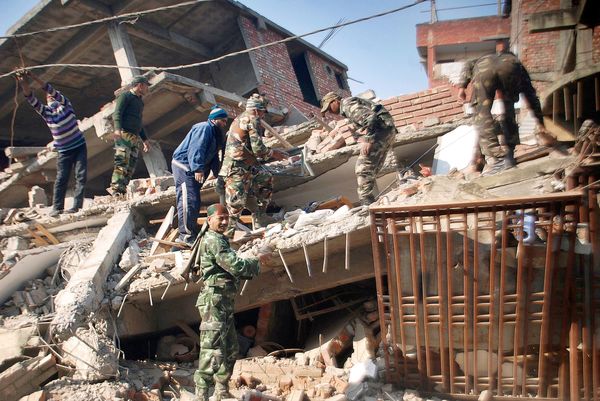

On January 4, 2016, a magnitude 6.7 earthquake struck the state of Manipur in northeast India, killing at least 11 people and causing significant damage to buildings and infrastructure in the region.
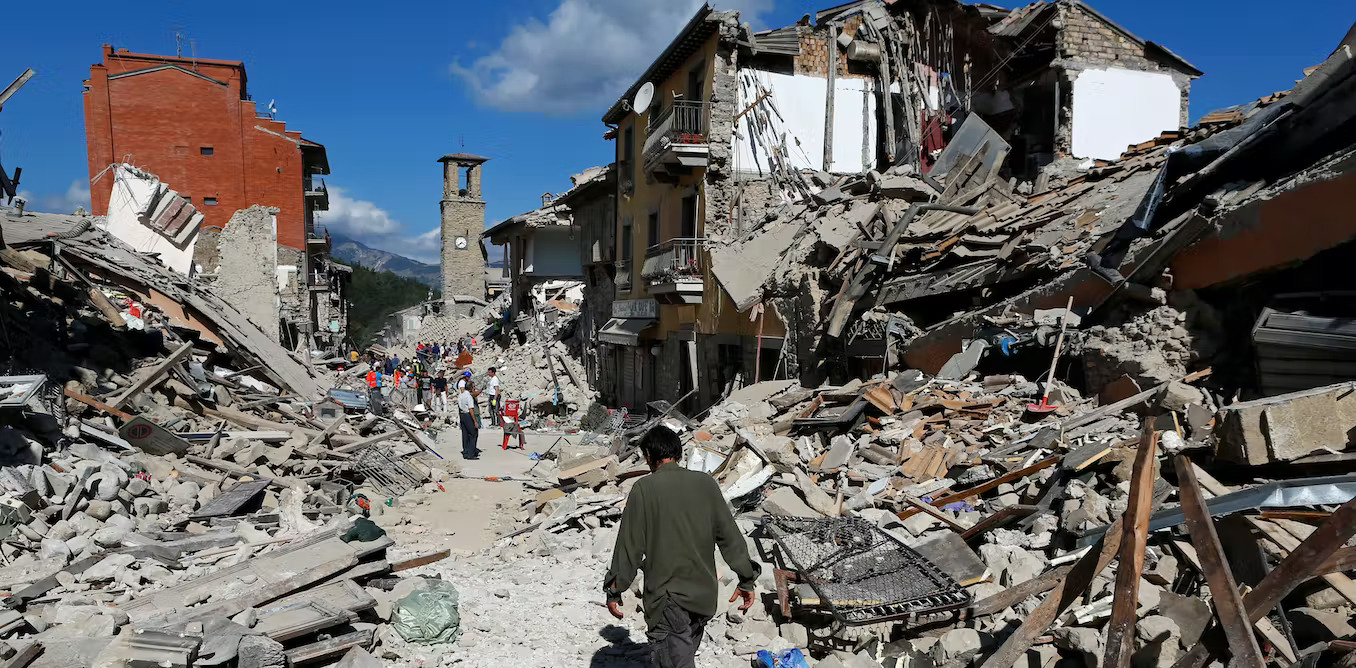
2016 Central Italy Earthquake
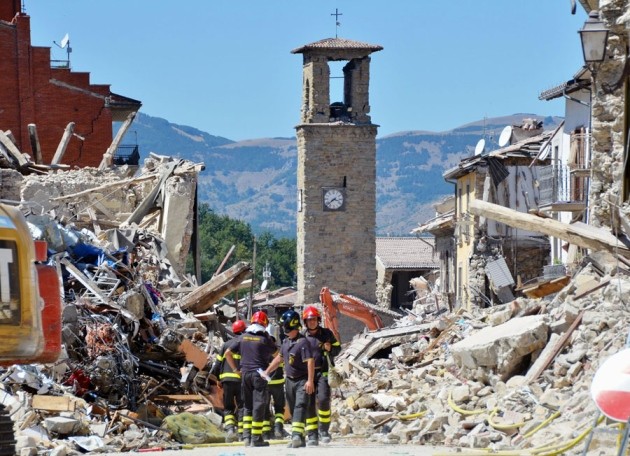

On August 24, 2016, a 6.2 magnitude earthquake damaged buildings and infrastructure in central Italy. The earthquake killed nearly 300 people and also injured hundreds more. Moreover, it destroyed several historic towns in the region.
Earthquakes remind us to prepare and respond. Ongoing research and monitoring is important. Although Scientists made progress, but earthquakes still cause damage. They are a natural hazard and also can be deadly.
To mitigate the impact of earthquakes, communities and governments must prepare by developing response plans and reinforcing vulnerable buildings. By doing so, they can reduce the potential damage and loss of life caused by these natural disasters. Additionally, research and monitoring can help predict and prepare for future earthquakes. Therefore, it is essential to remain vigilant and invest in preparedness measures to mitigate their impact.