THE EVOLUTION OF MONKEYS THROUGH THE AGES
Monkeys are a fascinating group of primates that have been evolving for millions of years. From their earliest ancestors to the diverse array of species we see today, they have adapted to their environments in unique ways. Here, we will explore the evolution of monkeys through the ages.
Early Monkey Ancestors
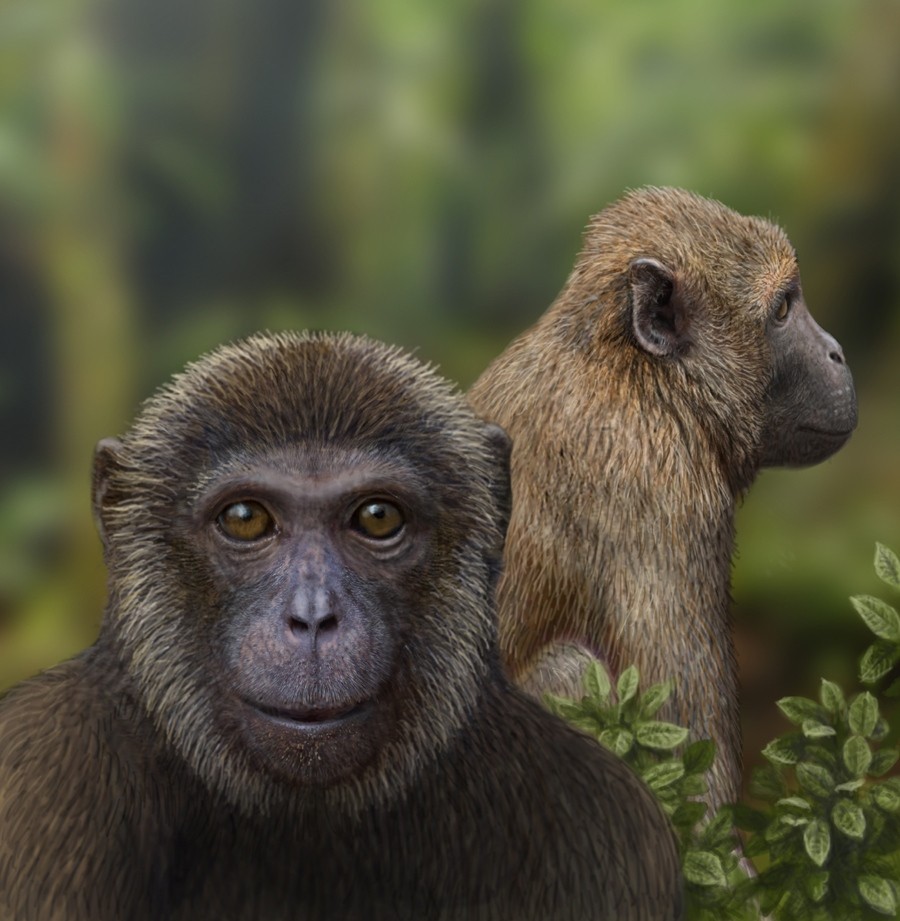
The earliest monkey ancestors appeared about 40 million years ago, during the Eocene epoch. These primates were small, arboreal creatures that lived in trees and fed on insects and fruit. They had grasping hands and feet, and forward-facing eyes that allowed them to see in three dimensions. Aegyptopithecus, which lived in what is now Egypt, is one of the most well-known early monkey ancestors.

New World Monkeys
Around 35 million years ago, monkeys began to evolve into two distinct groups: Old World and New World monkeys. New World type, found in Central and South America, possess a prehensile tail that they use to grasp objects and have their nostrils positioned to the side instead of facing forward, distinguishing them from Old World type.
New World Species possess a prehensile tail that they can use to grasp objects and have their nostrils positioned to the side rather than facing forward, which distinguishes them from Old World Species. They are found in Central and South America.
They also have specialized teeth that allow them to feed on tough, fibrous plant material.
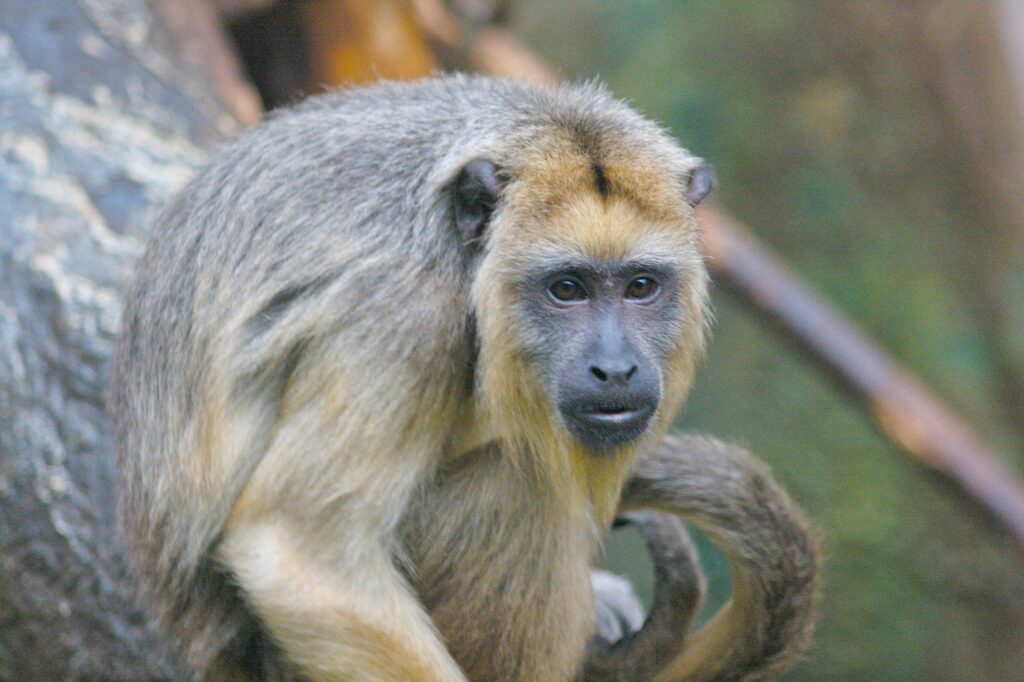

One of the most interesting New World type is the howler monkey. Their loud vocalizations, which can be heard up to three miles
Old World Monkeys
Old World monkeys are found in Africa and Asia, and they are more closely related to apes and humans than they are to New World monkeys. They have a tail that is not prehensile and nostrils that face forward. They are also adapted to a more varied diet than New World monkeys, and their teeth reflect this adaptation.
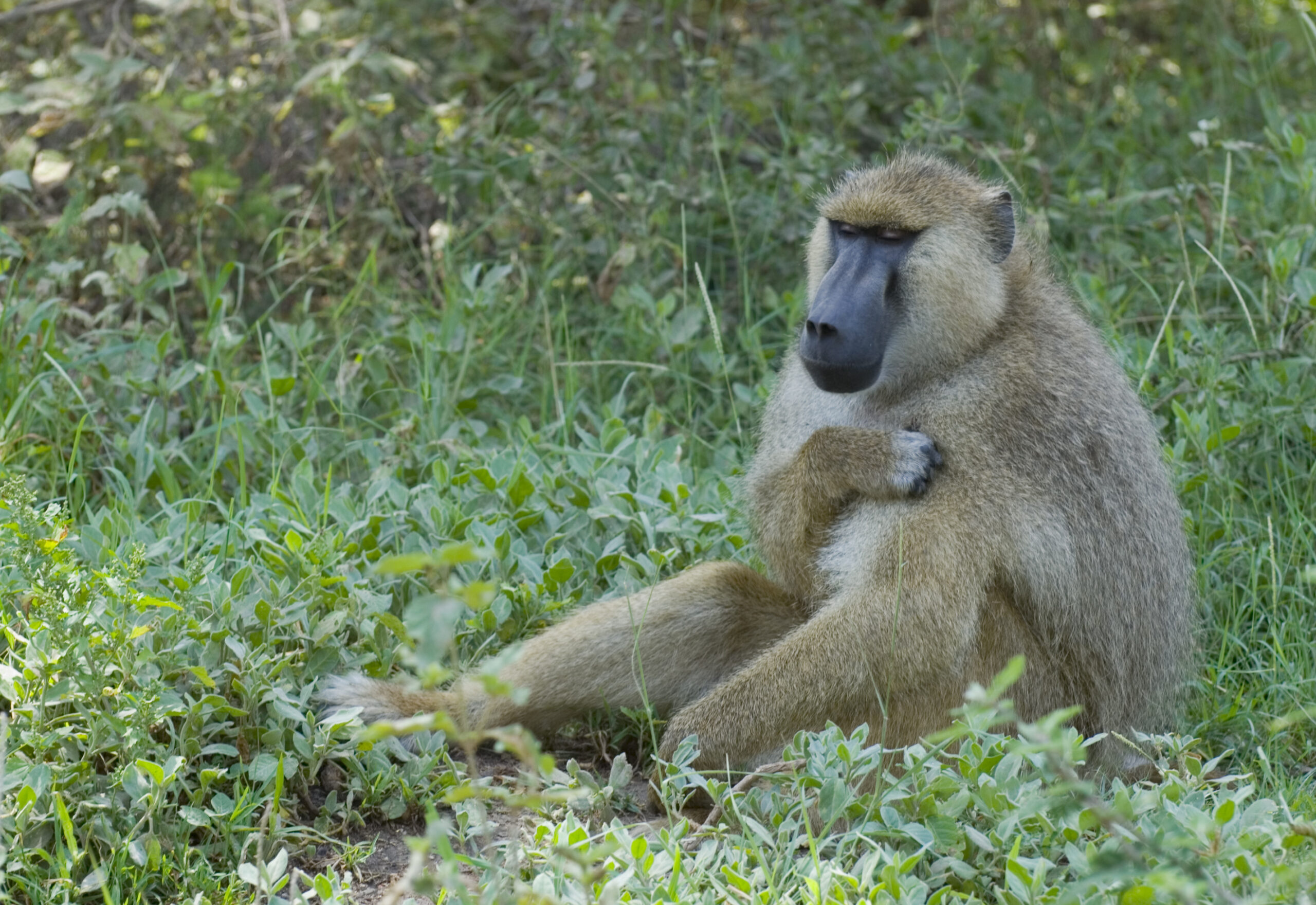

One of the most well-known Old World species is the baboon. Baboons are social animals that live in large troops and have a complex social hierarchy. Their distinctive facial features, which include a pronounced snout and long, sharp canine teeth, set them apart.
Human Evolution
Humans are also classified as primates, and we are closely related to both Old World Species and apes. In fact, our closest living relative is the chimpanzee. Humans evolved from a common ancestor with chimpanzees about 6 million years ago, and we share about 98% of our DNA with them.

As we can see, monkeys have been evolving for millions of years, adapting to their environments in unique ways. Today, there are over 260 species of monkeys each with their own special adaptations and behaviours. Studying the evolution of monkeys can help us understand our own evolution as primates, and the remarkable diversity of life on our planet.
Fascinating Facts About Monkeys
Monkeys are one of the most diverse and interesting groups of animals on the planet. From their social behaviour to their unique physical adaptations, there are many fascinating facts to learn about these primates. Here, we will explore some of the most interesting and surprising facts about monkeys.
Diversity of Monkeys
Monkeys inhabit various parts of the world, including the rainforests of South America and the mountains of Asia and Africa.
There are over 260 species of monkeys, ranging in size from the pygmy marmoset, which is only 4.6 inches long, to the mandrill, which can weigh up to 120 pounds.
Physical Adaptations
Monkeys have opposable thumbs and grasping hands and feet, which allow them to climb trees and manipulate objects with ease.
Some monkeys have prehensile tails, which means they can use their tails like an extra hand to grasp branches or objects.
Monkeys are strong and agile creatures with sharp teeth and claws, which can make them particularly effective at damaging objects or structures if they choose to do so.
Social Behavior
Monkeys are social animals that live in groups called troops. These groups can range in size from just a few individuals to over 100.
Monkeys’ vocalizations can vary from loud alarm calls to soft purring sounds, which is a well-known characteristic of these animals.. Some species, like the howler monkey, have particularly loud calls that can be heard for miles.
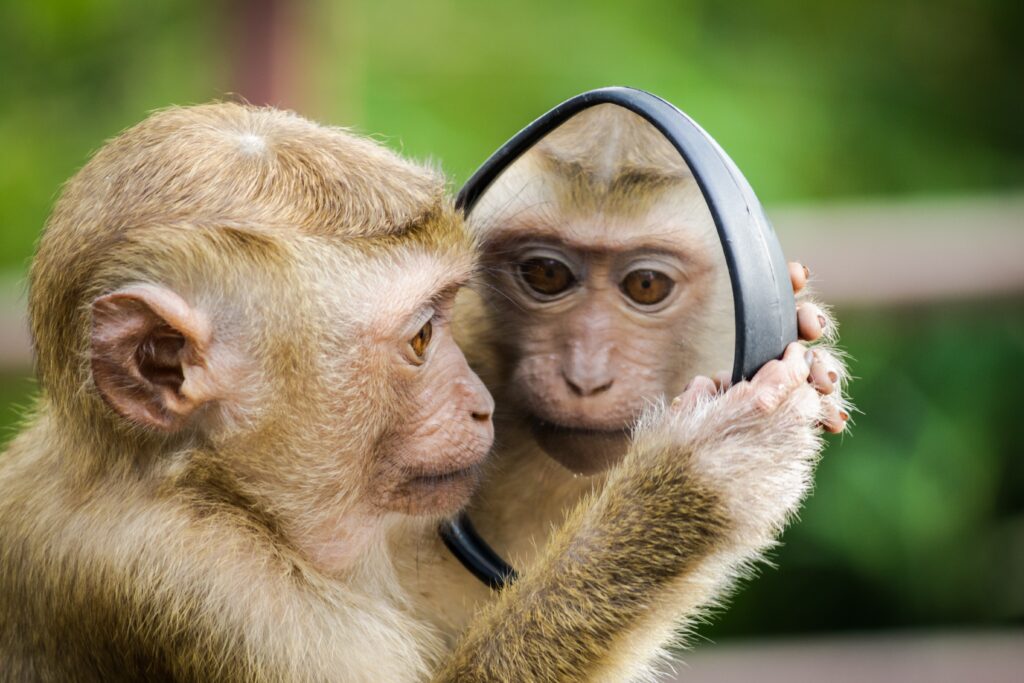
Monkeys’ intelligence is evident through their ability to use tools, solve puzzles, and recognize themselves in mirrors, as observed by researchers.
Diet and Habits
The diet of monkeys can vary depending on the species, habitat, and availability of food. Generally, most of them are omnivores, which means they eat both plants and animals.
Some Species primarily eat fruit, while others may eat insects, small mammals, or even other monkeys.
Monkeys have specialized teeth and digestive systems that allow them to process a variety of foods.
Curious and Fascinating Facts About Different Species of Monkeys
Monkeys are some of the most intriguing and captivating creatures on the planet. Their unique physical features, social behaviour, and habits make them a subject of fascination for people of all ages. From the tiny pygmy marmoset to the enormous mandrill, there are many curious and fascinating facts to learn about different species of monkeys.
Pygmy Marmoset
Pygmy Marmosets are the smallest monkeys in the world, weighing only 4-5 ounces as adults.
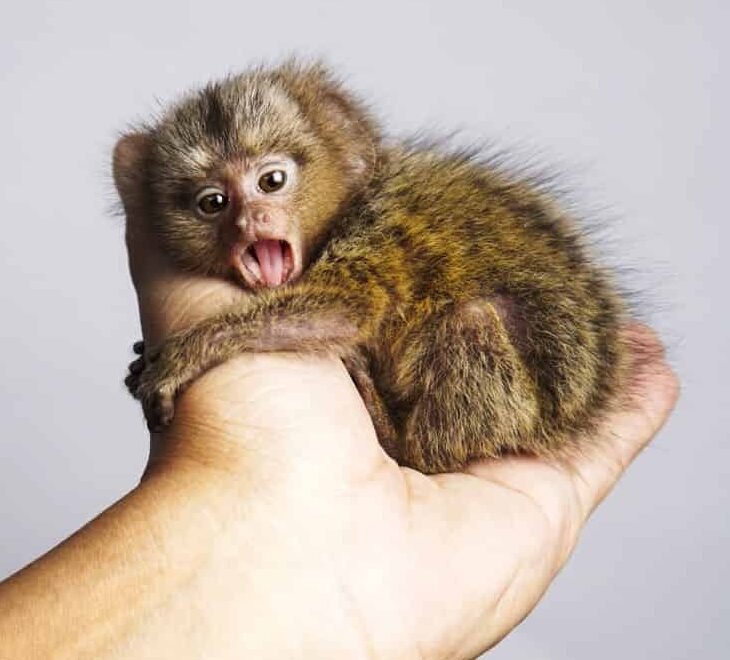

They are found in the rainforests of South America and have distinctive white ear tufts. They communicate with each other using a unique language of high-pitched squeaks and trills, and primarily eat insects and tree sap.
Mandrill
Mandrills are the largest species of monkey in the world, with males weighing up to 120 pounds.

They are found in rainforests in Central and West Africa and are known for their brightly coloured faces. A mandrill uses the colours on its face to communicate social status and attract mates, which can range from blue and purple to red and yellow. They primarily eat fruits, but will also consume insects and small animals.
Proboscis Monkey
Proboscis monkeys are found only on the island of Borneo and are known for their long, bulbous noses which can grow up to 7 inches in length.
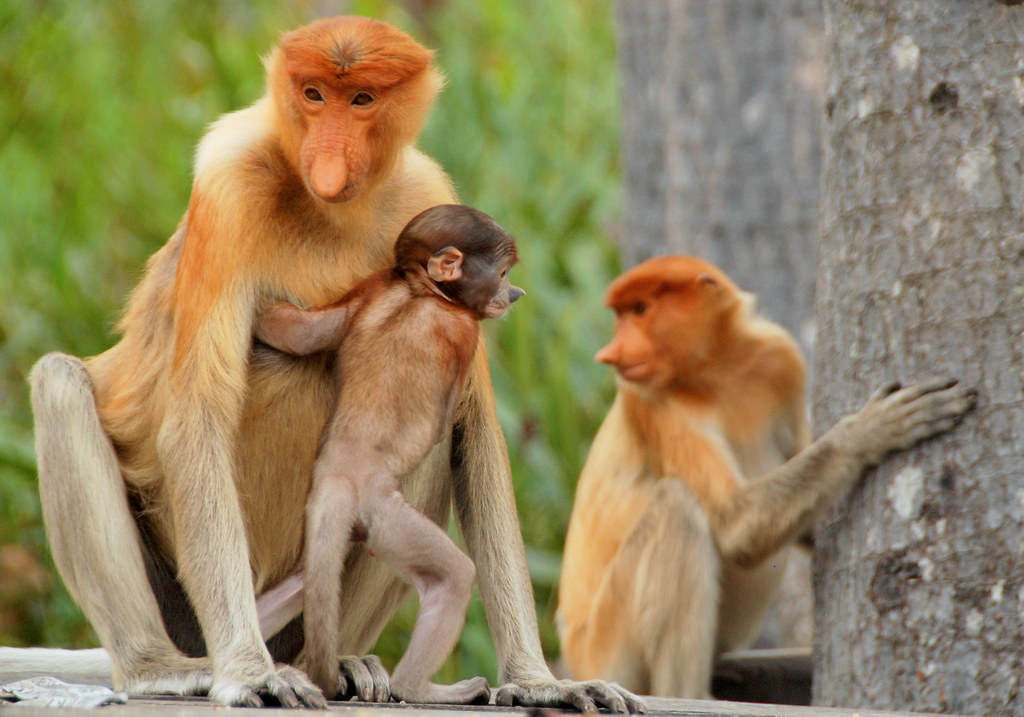

They primarily eat leaves, seeds, and unripe fruits, and are excellent swimmers, using their webbed feet to dive underwater to escape predators and find food.
Howler Monkey
These monkeys are famous for their loud vocalizations that can be heard from over 3 miles away.
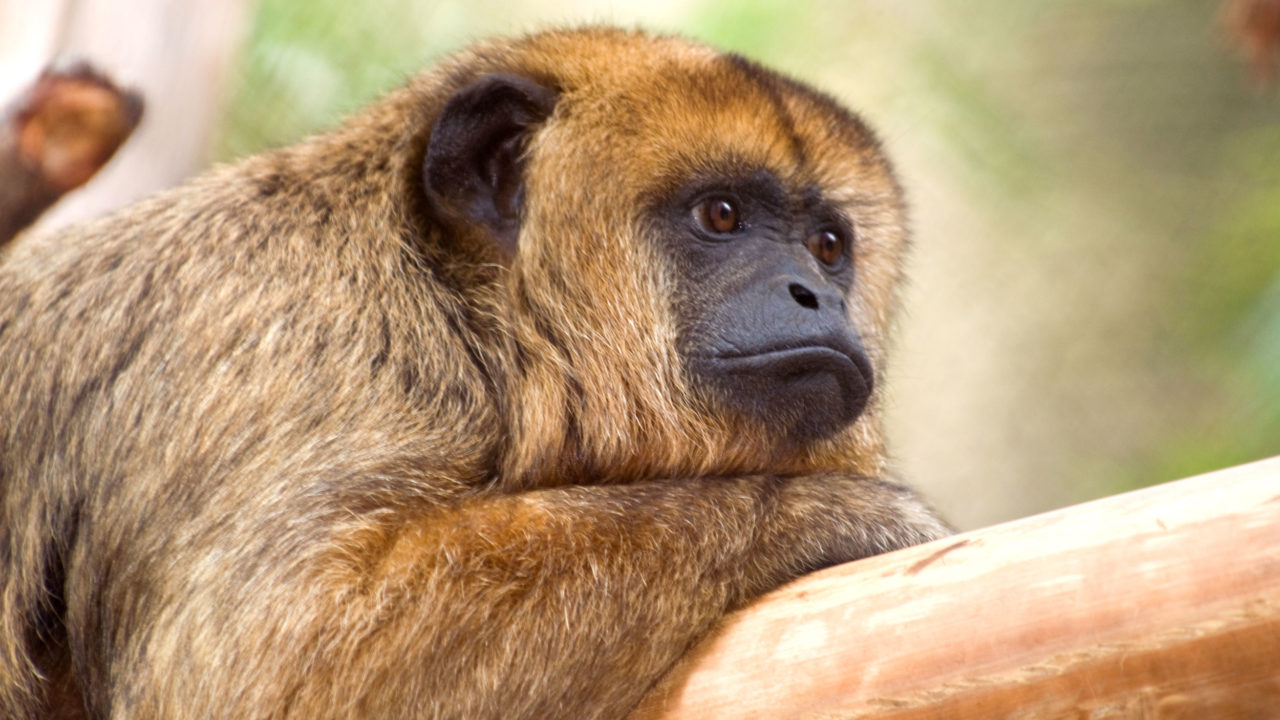

They use their distinctive calls to communicate with other members of their troop and mark their territory.
Gelada
Gelada monkeys are Found only in the Ethiopian Highlands, these monkeys have a unique hourglass-shaped patch of skin on their chest that turns bright red during mating season.

They communicate through a complex system of vocalizations, facial expressions, and body language.
Japanese Macaque
These monkeys can survive in extremely cold temperatures, and to keep themselves warm, they’ve been observed soaking in hot springs.
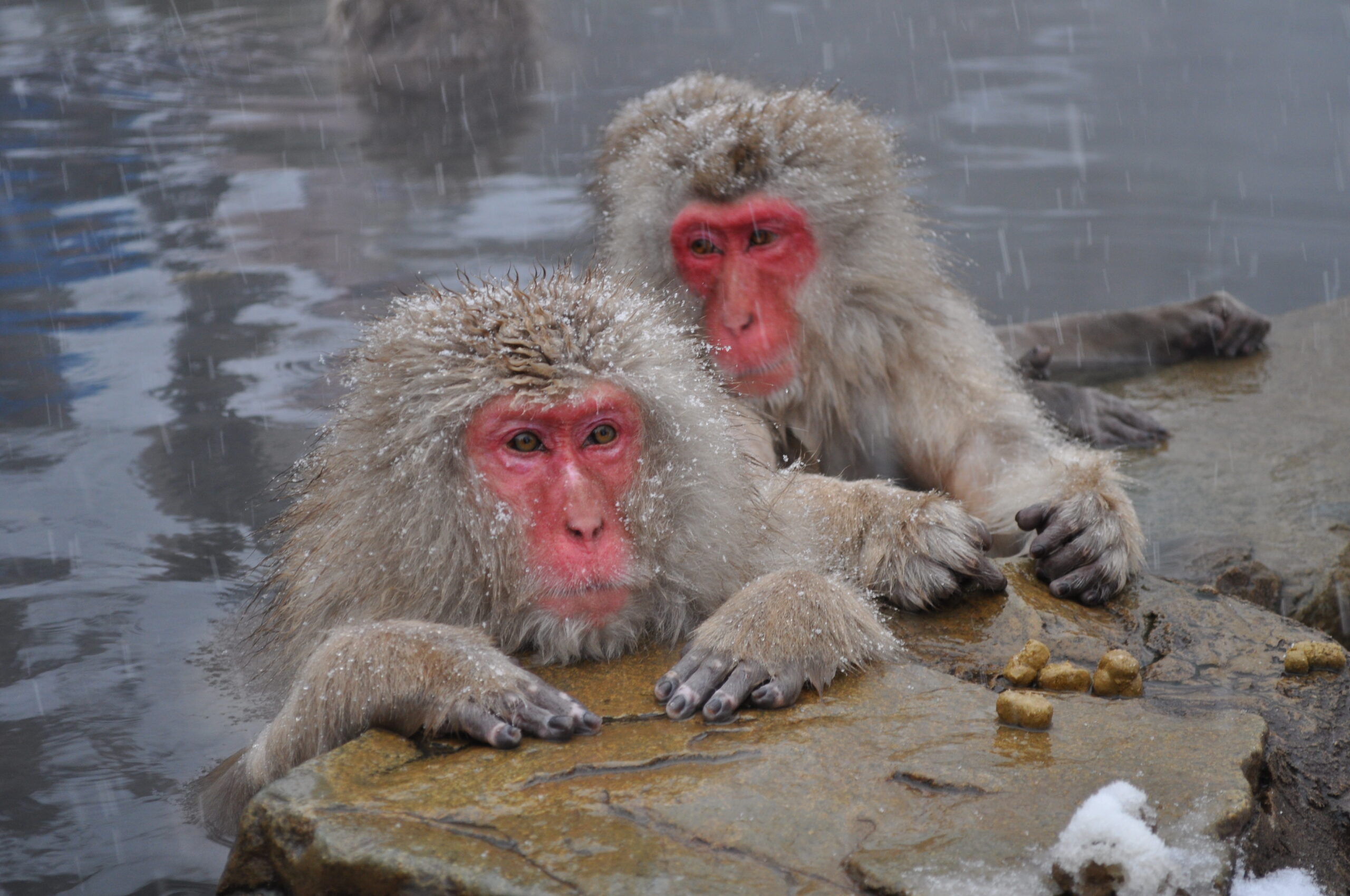

They’re also intelligent and have been seen using tools to help them obtain food.
Capuchin Monkey
Capuchin monkeys are incredibly resourceful and have been seen using rocks and sticks to help them obtain food.
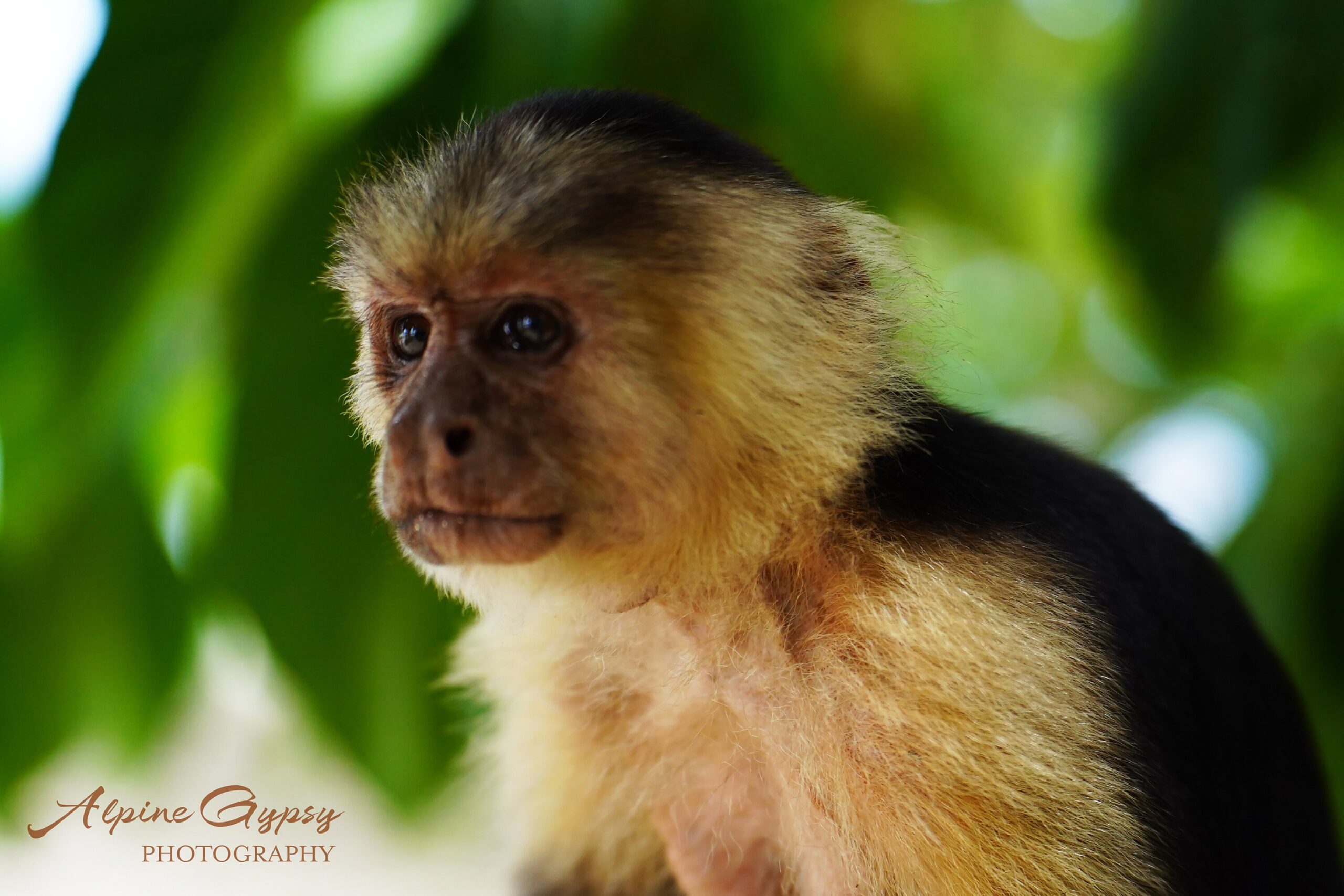

They can crack open nuts and shells with rocks and even use sticks to fish insects out of tree bark.
Squirrel Monkey
These small, agile monkeys are known for their playful behaviour and acrobatic skills.
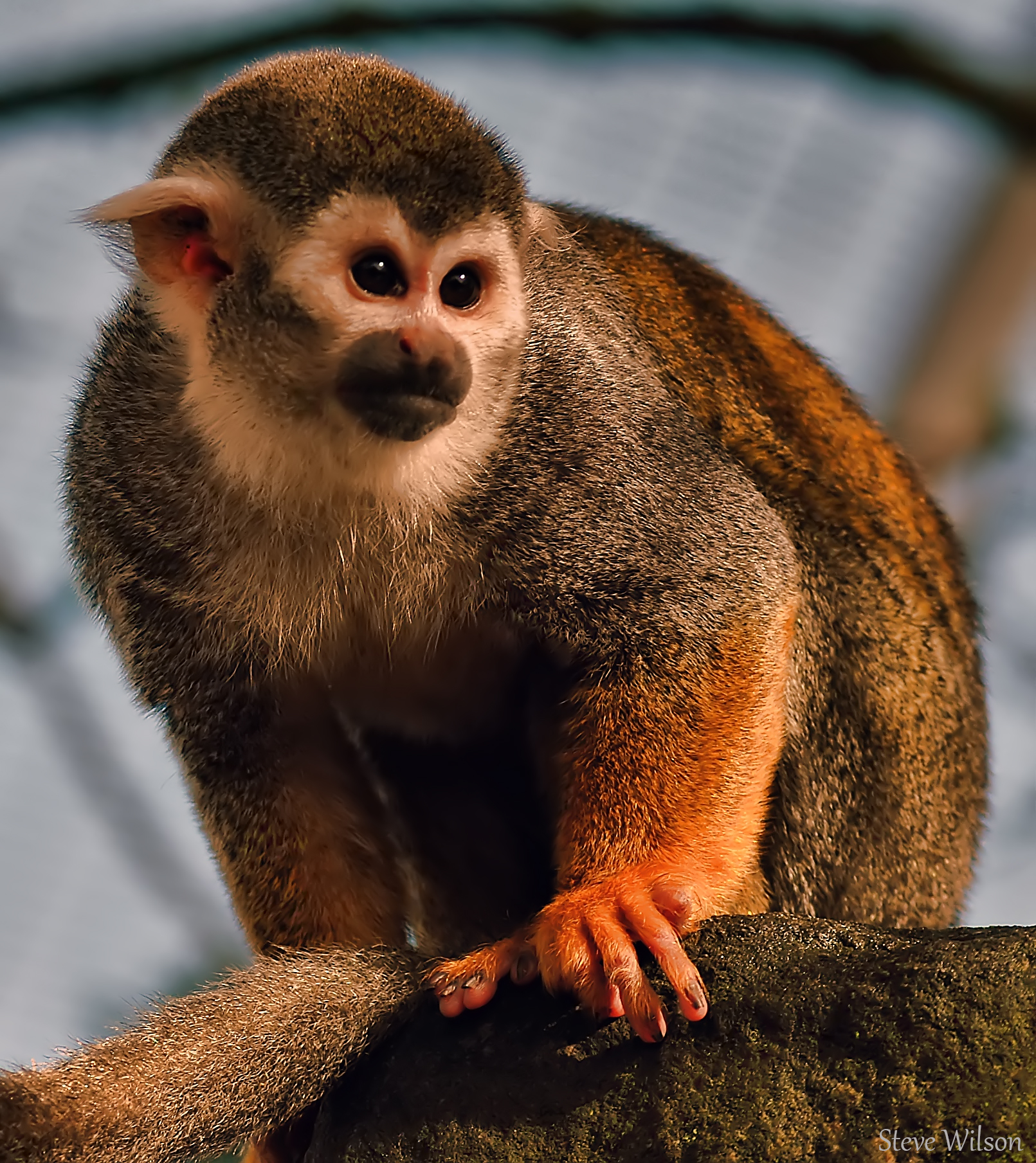

They are native to Central and South America and have distinctive markings around their eyes.
Tarsier
Tarsiers are tiny primates with huge eyes and long, thin fingers.
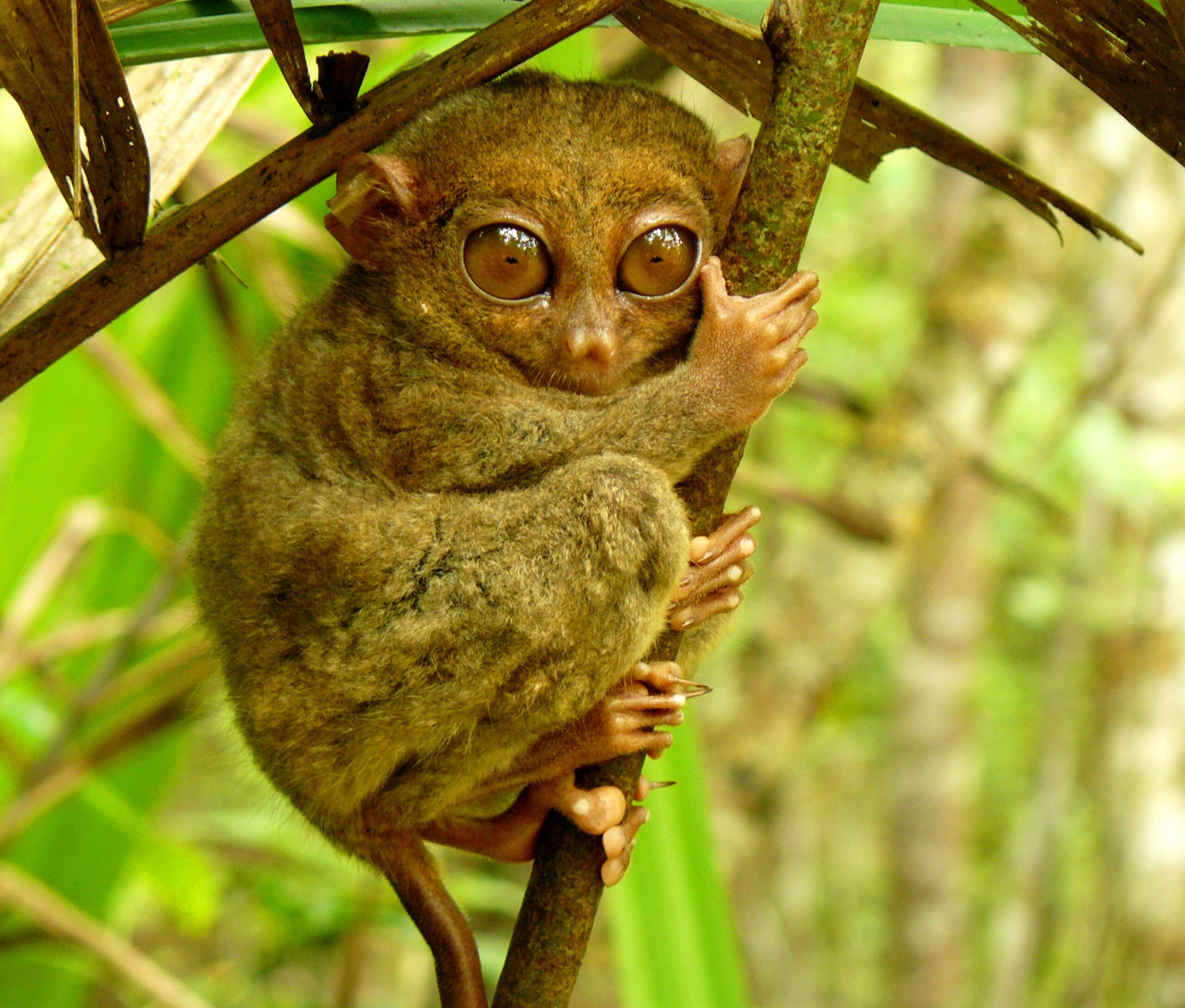

Their unique vocalizations are a well-known characteristic of the primates that are native to Southeast Asia
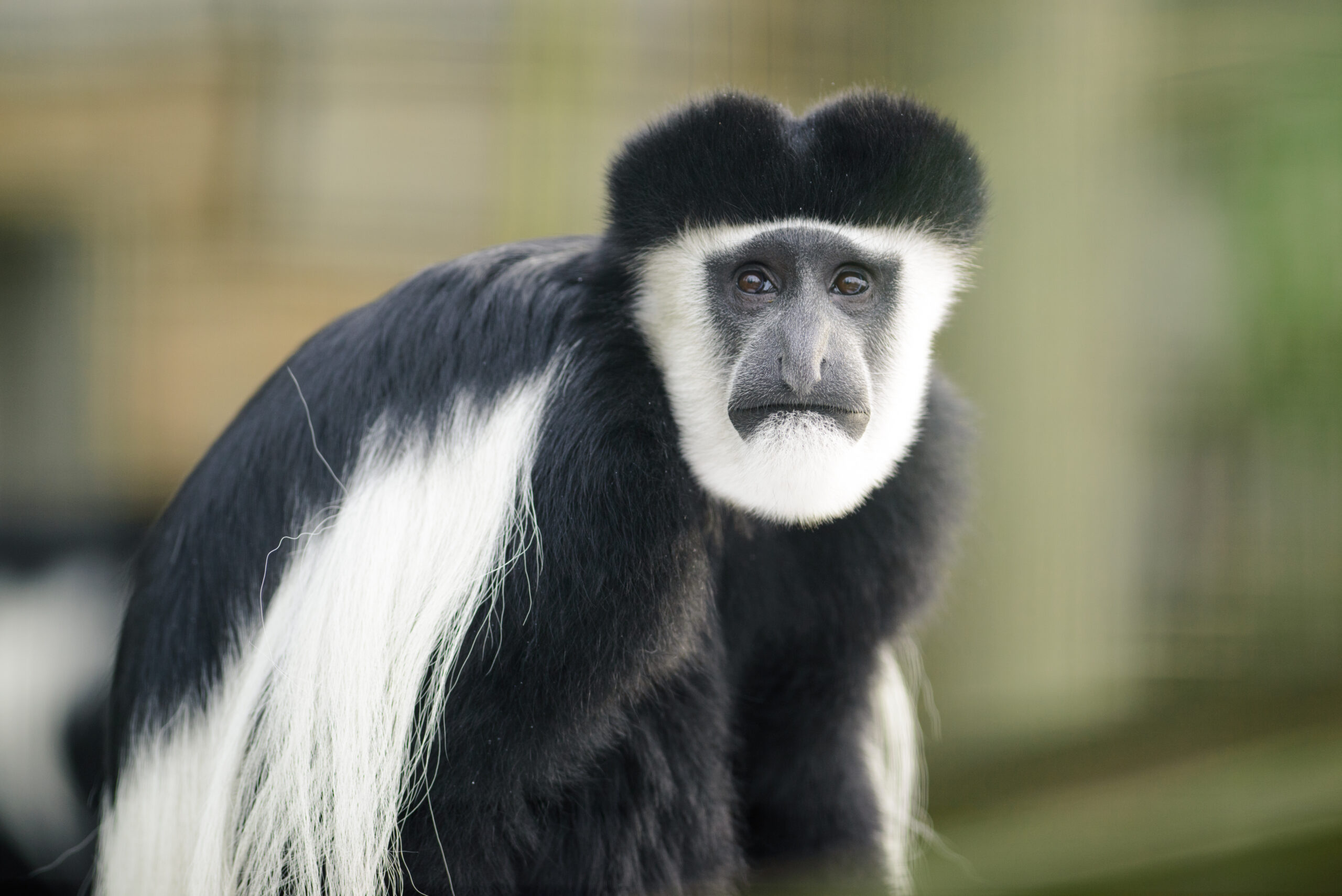
Colobus Monkey
These monkeys have long, silky hair and a distinctive white beard. They have impressive leaping abilities and inhabit various regions of Africa.

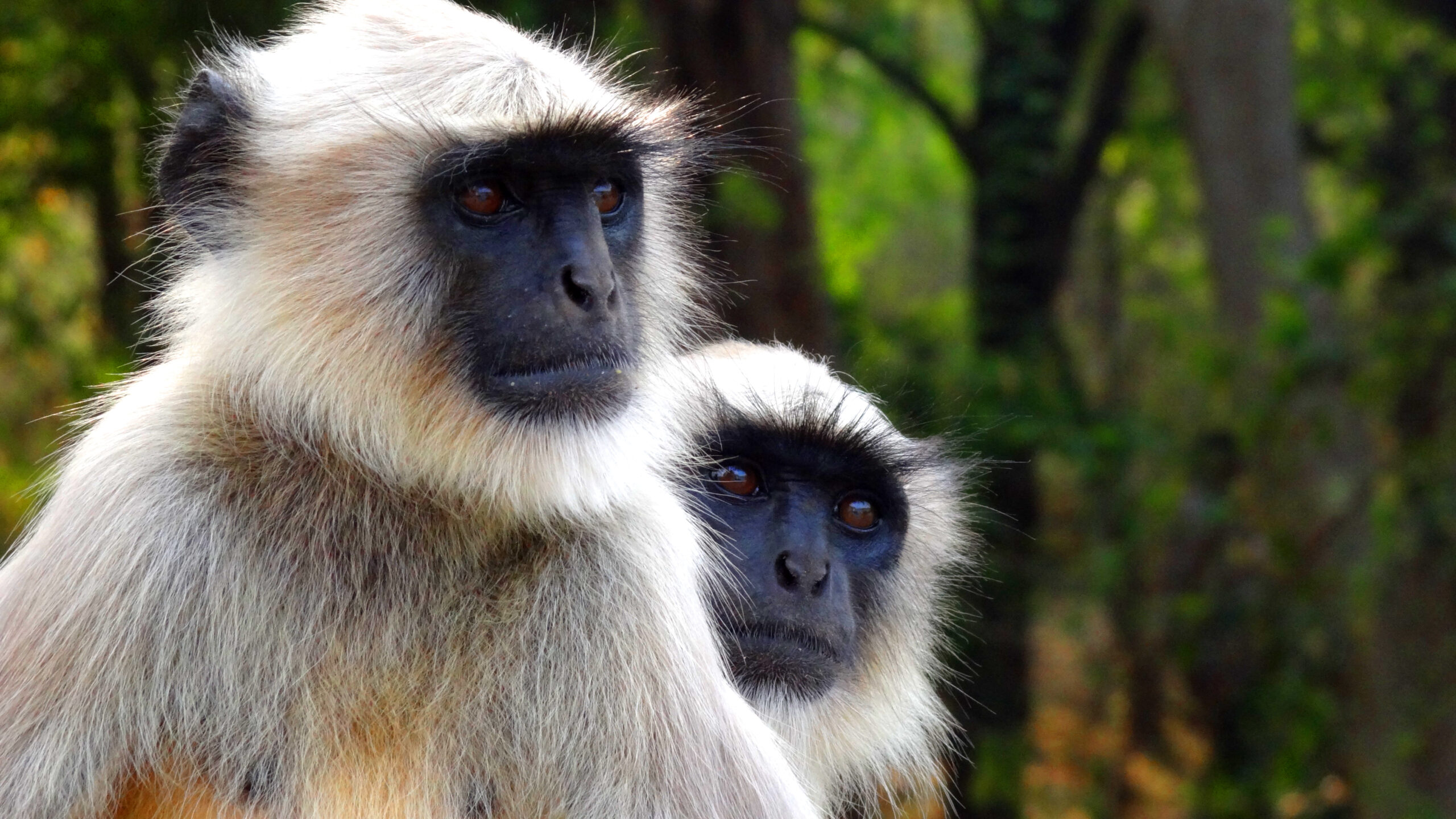
Langur
Langurs are large, majestic monkeys with long tails and a distinctive crest of hair on their heads.

Macaques found in Asia exhibit a notable feature of being able to produce loud, melodious calls.
Vervet Monkey
These monkeys inhabit the rainforests of Brazil and display a unique blue face, which is a notable characteristic. Additionally, they are also known for their social behaviour.
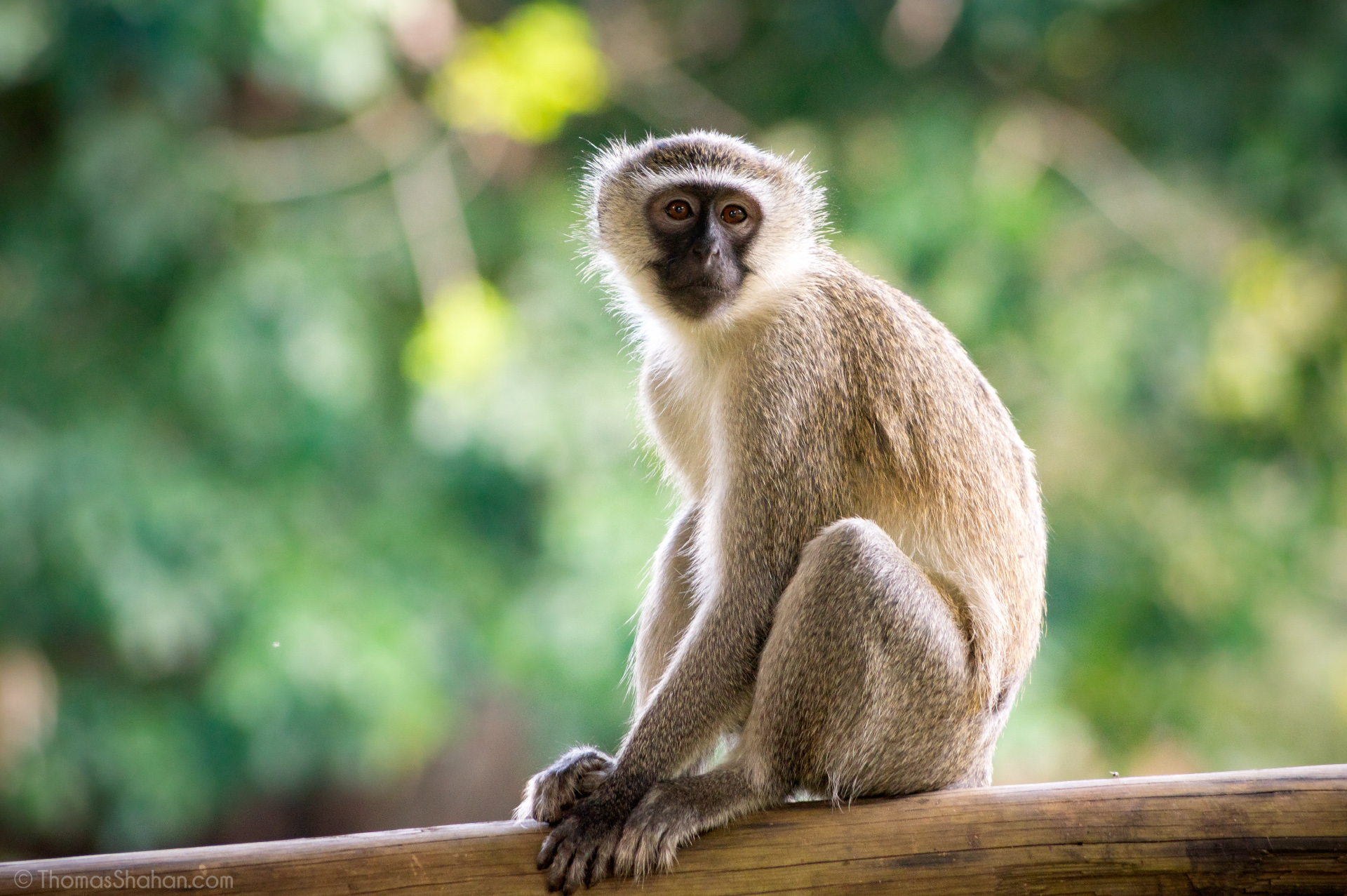

They are found in Africa and are often kept as pets.
Golden Lion Tamarin
The rainforests of Brazil are home to these small, brightly coloured monkeys.

Macaque
Macaques exist as a group of primates found throughout Asia and Africa.
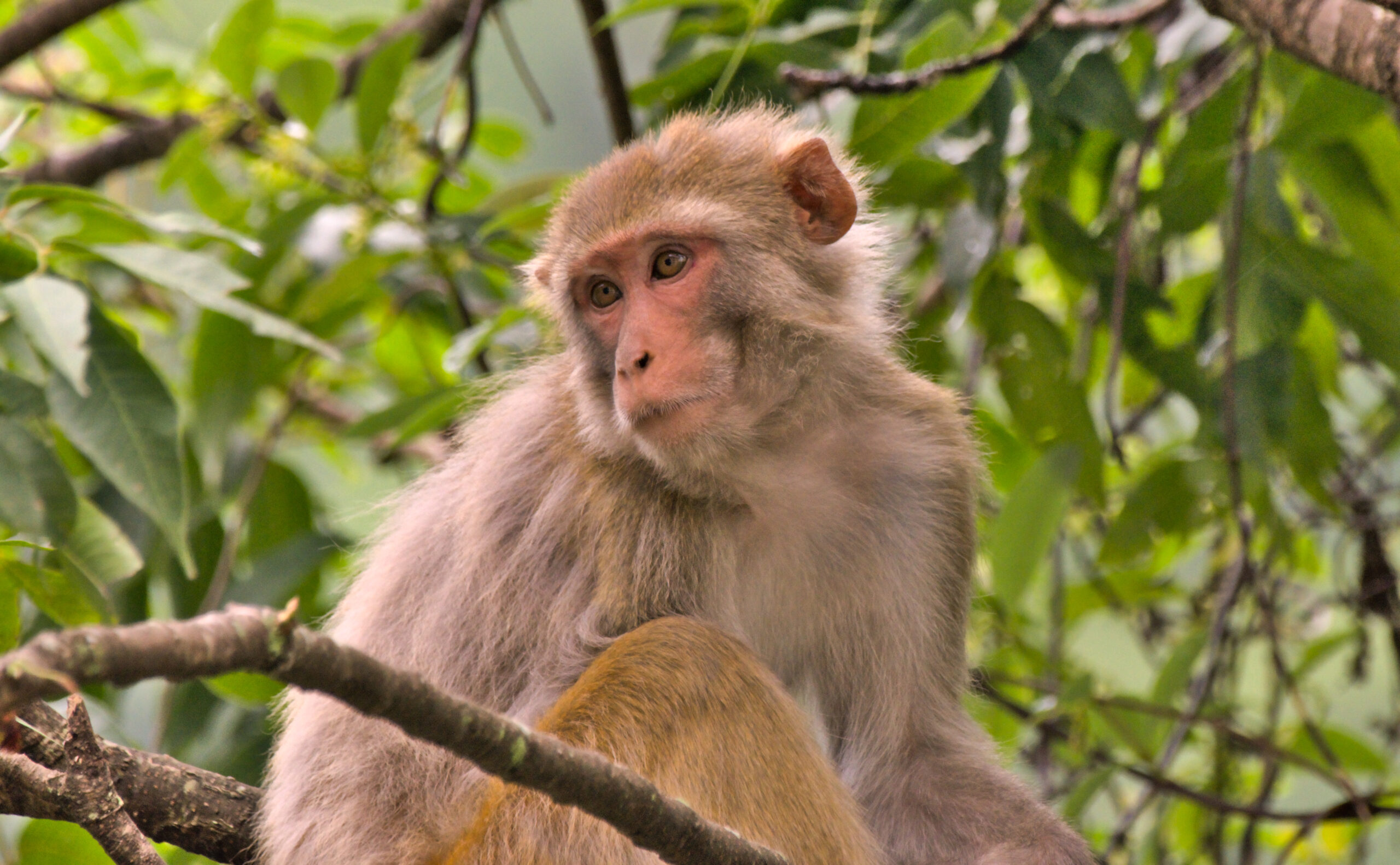

Researchers have observed monkeys using tools and solving complex problems, which has made their intelligence well-known.
These are just a few examples of the many different types of Species in the world. Each species has its unique characteristics and behaviours, making them a fascinating subject of study and observation.
Monkeys as carriers of diseases
Monkeys can carry a variety of diseases, including herpes B virus, which can be deadly to humans. Bites and scratches are the means of transmission for the virus, and those who work closely with them, like zookeepers and researchers, are at risk of contracting the virus. In addition, they can also carry parasites, such as ticks and lice, which can cause further health issues.
Monkeys as predators of wildlife
Monkeys prey on smaller animals, such as birds and lizards, as they are opportunistic predators. Their hunting behaviour can affect local ecosystems and disrupt the balance of wildlife populations. In some cases, they have also attacked and killed larger animals, such as goats and sheep.
Monkeys as disruptors of urban areas
As urbanization continues to expand, monkeys are increasingly coming into contact with humans and urban environments. They can cause damage to buildings and vehicles, and their presence can also lead to safety concerns. Some Species attack humans when humans encroach upon their natural habitats or when they feel threatened.
Monkeys are Destructive
Hunger or Thirst
Monkeys require a lot of food and water to sustain their energy levels, and if they are unable to find sufficient resources in their natural habitat, they may resort to destructive behaviour to obtain food or water.
Boredom or Lack of Enrichment
In captivity, they may become bored or stressed if they do not have enough opportunities to engage in natural behaviours such as climbing, foraging, and socializing. This can lead to destructive behaviour such as chewing on objects or dismantling their enclosure.
Human Interactions
Human activities such as feeding, harassing, or capturing them can also contribute to destructive behaviour. They may become reliant on human food and lose their natural foraging skills, or become aggressive towards humans if they feel threatened or harassed.
monkeyS are known as cheaters or copy things
Monkeys possess intelligence and are capable of learning from one another. Observations have shown that some species, including capuchin monkey, imitate the behaviours of other individuals within their group.. This can include copying the way they use tools to solve problems or copying the way they communicate with each other.
Overall, while they may exhibit behaviours that could be perceived as “cheating” or copying, it’s important to remember that these behaviours are often a result of their natural intelligence and social dynamics within their groups.
MONKEYS ARE DANGEROUS
monkeys funny activities
Monkeys’ playful and social nature allows them to display a variety of behaviours that humans may find entertaining or amusing. Some examples of funny or playful activities that they may engage in include
Playful grooming
Monkeys often groom each other as a way of bonding and socializing. This can include playfully pulling on each other’s fur or tickling each other.
Acrobatic feats
Many species of monkeys are excellent climbers and can perform impressive acrobatic feats such as swinging from branches, leaping between trees, and balancing on narrow surfaces.
Mimicry
Some species of monkeys are able to mimic human speech or other sounds, which can be amusing to observe.
Playful aggression
Monkeys may engage in playful fights or mock battles as a way of establishing dominance or practicing social skills. This can include chasing each other, playfully biting or grabbing, or wrestling.
Curiosity and exploration
Monkeys are curious animals and may investigate objects or environments in playful ways. This can include playing with toys, exploring new areas, or interacting with unfamiliar objects.
Monkeys are fascinating animals that play an important role in the ecosystem. They are intelligent, social, and playful creatures that have captured the hearts of people all over the world. However, their populations are under threat, and it is up to us to take action to protect them and their habitats. By doing so, we can ensure that these amazing animals continue to thrive for generations to come.